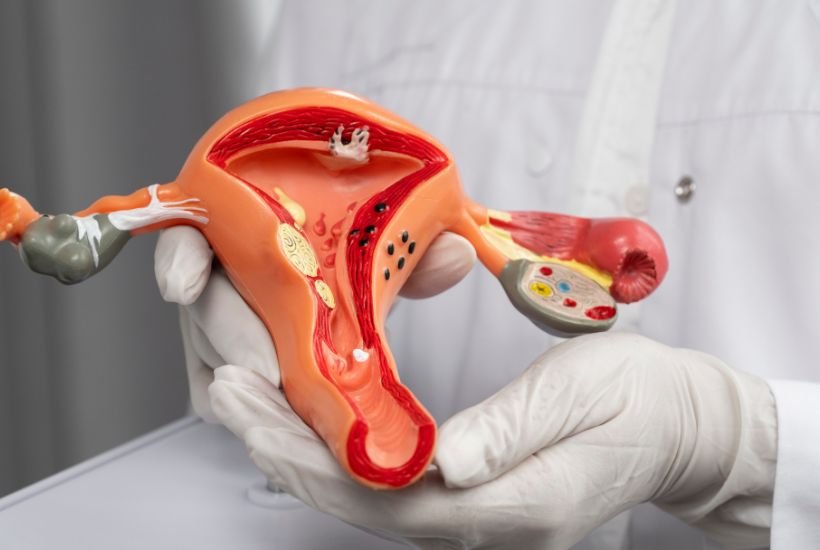
Gynecology is a vital branch of medicine dedicated to the health of the female reproductive system. This medical specialty focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases and disorders affecting the vagina, uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and breasts. Gynecology plays a crucial role in women’s overall health, addressing a wide range of issues from menstrual problems and infections to reproductive health and cancer screening. The field also covers surgical procedures designed to treat various gynecological conditions, ensuring women receive comprehensive care throughout different stages of life.
At the core of gynecology is the management of menstrual problems. Many women experience irregular periods, heavy bleeding, or painful menstruation, medically known as dysmenorrhea. Gynecologists help diagnose the underlying causes of these symptoms and recommend treatments that may range from hormonal therapies to lifestyle changes. Addressing menstrual irregularities is important not only for comfort but also for detecting potential health concerns that could impact fertility and long-term well-being.
Reproductive health is another critical aspect of gynecology. This includes fertility evaluations, contraception advice, pregnancy care, and management of menopause. Gynecologists often collaborate with obstetricians to provide care for women during pregnancy and childbirth, highlighting the close relationship between gynecology and obstetrics. Fertility issues are a common reason women seek gynecological care, and specialists use a variety of diagnostic tools and treatments to help individuals or couples conceive. Contraception counseling helps women choose safe and effective methods to prevent unwanted pregnancies and manage reproductive goals.
Infections affecting the female reproductive system are frequent concerns in gynecology. Common issues include yeast infections, bacterial vaginosis, and sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as chlamydia and gonorrhea. Gynecologists conduct screenings, provide treatments, and offer preventive guidance to reduce the risk of infection and protect reproductive health. Regular check-ups and safe sexual practices are often emphasized during gynecological visits to maintain overall well-being.
Cancer screening and treatment form a significant part of gynecological care. Early detection of cancers such as cervical, ovarian, uterine, and breast cancer improves treatment outcomes. The Pap smear, or Pap test, is a well-known screening procedure used to detect cervical cancer and precancerous changes in cervical cells. Alongside this, pelvic exams and imaging tests like ultrasounds help monitor reproductive organs for abnormalities. When necessary, gynecologists may perform procedures such as colposcopy, which offers a detailed examination of the cervix, or hysteroscopy, which allows visualization of the inside of the uterus. These tools are essential for diagnosing and managing gynecological cancers and other serious conditions.
Pelvic pain and disorders like endometriosis and fibroids are common reasons women visit gynecologists. Endometriosis occurs when tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus, causing pain and sometimes infertility. Fibroids are benign tumors in the uterus that can lead to heavy menstrual bleeding and discomfort. Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), an infection of the reproductive organs, can also cause pain and complications if untreated. Gynecologists use a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging, and sometimes surgical intervention to treat these conditions and improve quality of life.
Surgical procedures are an important part of gynecological practice. Hysterectomy, the removal of the uterus, may be necessary for conditions like uterine fibroids, cancer, or severe bleeding. Minimally invasive surgeries such as laparoscopy allow gynecologists to diagnose and treat issues with smaller incisions, leading to faster recovery times. Tubal ligation, a permanent contraception method, is another common gynecological surgery.
Gynecologists are highly trained medical doctors who specialize in this field. Many also practice obstetrics, offering comprehensive care from reproductive health to pregnancy and childbirth. Together, they are often referred to as OB/GYNs. Their expertise ensures women receive personalized and evidence-based care tailored to their unique health needs.
The importance of gynecology extends beyond treatment. Regular gynecological care helps with early detection of diseases, management of hormonal changes, and education on sexual and reproductive health. It supports women through puberty, reproductive years, pregnancy, and menopause, helping maintain physical and emotional well-being.
Gynecology is closely linked to other medical specialties such as reproductive endocrinology, which focuses on hormonal functioning related to reproduction, and oncology, which deals with cancer treatment. Advances in medical technology, including ultrasound imaging and minimally invasive surgery, have improved the effectiveness and safety of gynecological care.
Historically, gynecology has evolved over centuries. Early records of women’s health treatments exist from ancient civilizations such as Egypt, Greece, and Rome. Modern gynecology benefits from centuries of medical research and innovation, constantly advancing to provide better care and improve outcomes for women worldwide.